How to erase your iPhone, iPad, or Mac remotely after a theft
[ad_1]
One of the most powerful features added years ago to macOS and iOS was Find My iPhone—and iPad and Mac. The iCloud-connected service lets you track an accidentally misplaced item and potentially recover a stolen one.
With the service active on a device, you can use Find My for macOS, iOS, or iPadOS or via iCloud.com to erase your computer, phone, or tablet or to queue an erasure signal for the next time the device is on the Internet.
iPhones and iPads with a Secure Enclave and Macs with FileVault enabled simply delete the encryption keys for storage. This renders the data irretrievable. (It doesn’t affect your local or iCloud backups, so don’t worry.) On a Mac with a T2 Security Chip or M1 Apple silicon, disk encryption is always enabled even if FileVault isn’t, allowing Secure Enclave to destroy the disk encryption keys instantly even with FileVault disabled.
Pre-Secure Enclave iPhones and iPads and Macs that predate the T2 Security chip and have FileVault disabled take longer to delete files, as each byte of data has to be overwritten.
If you’re not sure whether your iPhone, iPad, or Intel Mac has a Secure Enclave, consult the list Apple provides here. You can determine if FileVault is enabled by going to the Security & Privacy preference pane’s FileVault tab.
How to erase a device
IDG
Apple’s tweaked the process slightly for its native apps but left iCloud.com virtually untouched for years.
In macOS, iOS, or iPadOS, launch the Find My app. Tap the Devices tab and then tap your hardware. (If you have Family Sharing enabled, you can also see the devices of family members.) On an iPhone or iPad, tap Erase This Device and follow the prompts. On a Mac, right-click the device and select Erase This Device.
With iCloud.com, log in to your account and click the Find iPhone link—no “My” in there. Enter your iCloud password again if prompted. Click the All Devices menu and select your hardware:
- For a Mac, click Erase Mac and follow prompts; you’ll note the text says it “may take up to a day to complete,” the worst-case example for a hard-drive-equipped Mac without FileVault enabled and neither a T2 nor M1 chip.
- For an iPhone or iPad, just click Erase iPhone or Erase iPad.
If the device is connected to the internet via whatever method it has at its disposal—Wi-Fi, cellular, tethering, a…dial-up modem—erasure begins immediately after the Mac receives the signal relayed via Apple’s servers. In the cases noted above, the drive or flash storage almost instantly becomes irretrievable.
The erase command is queued by Apple, so if the device ever is briefly back on the internet, it erases itself. Once your device starts wiping its data, finding its location via Find My is no longer possible.
For devices that ne’er-do-wells have taken offline or put in a metal box, they may never return online to receive an erase command. But for iPhones, iPads, and Macs with a Secure Enclave, the stored data can’t be interacted with unless someone also obtained the password. (For a running Mac, there might be cracks that work, but it’s unlikely; if powered down and FileVault is enabled, effectively impossible.)

It can be wiped, which securely removes your data—and then Activation Lock kicks, a part of Find My. (Macs have a few additional requirements.) Activation Lock prevents an erased device from being set up again without knowing the iCloud password associated with the account that turned on Find My on it.
Criminal groups have apparently figured out ways to bypass Activation Lock in at least some cases, but those methods still require erasing the device, so your data remains inaccessible.
A future of remote erasure?
I can imagine a future in which the Find My Network could be used to trigger erasure, too. Right now, the system is used entirely as a passive relay: an AirTag tracker and most Apple devices can broadcast their position over Bluetooth in a carefully encrypted manner. Nearby Macs, iPhones, and iPads with Find My Network enabled relay this data via Apple so you can get updates about location without the party relaying it knowing who you are or which device is transmitting.
But AirTags point the way to a potential two-way process. If Apple determines an AirTag has been traveling with you and you’re not the owner of it, you’re presented with a dialog on an iPhone or iPad that lets you play a sound. That command is passed via Bluetooth.
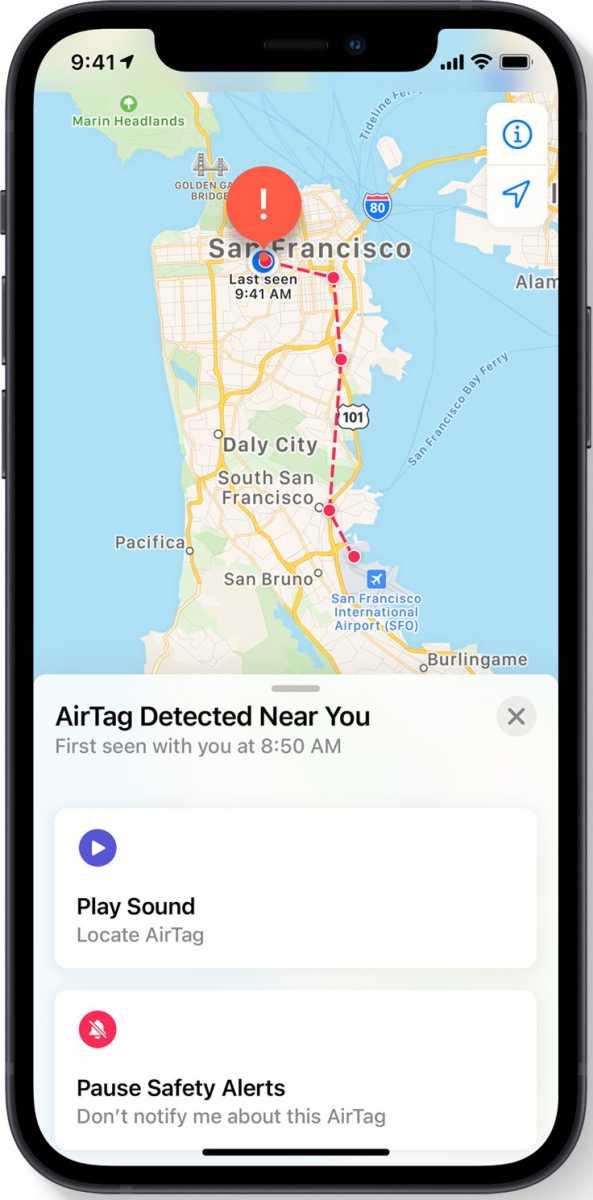
The COVID-19 exposure notification system points to a more complicated system that preserves privacy and yet could be turned to device erasure, too. In Apple and Google’s joint notification system, your smartphone recorded all specially formatted Bluetooth signals around you and retained for those a period of time; this is quite similar to the signals emitted for the Find My Network by Apple devices.
If someone who had been near you receives a COVID diagnosis and enters a code into their smartphone provided by their healthcare provider, the encrypted Bluetooth IDs associated would then be uploaded to a database that all devices in your region or country regularly downloaded and compared to stored IDs.
Now, consider this: what if you could report your device as stolen and that you wanted it erased. That signal would then be distributed in encrypted form across all Apple hardware in your area or an expanded region. If any of those devices picked up an encrypted Bluetooth signal that matched, they could transmit a similarly encrypted erasure instruction. Thieves try to disable all the wireless on a device, but Bluetooth is often harder to block than Wi-Fi or cellular.
The safeguards around this would have to be strong, but it’s not far-fetched—just far-reaching!
This Mac 911 article is in response to a question submitted by Macworld reader Romy.
Ask Mac 911
We’ve compiled a list of the questions we get asked most frequently, along with answers and links to columns: read our super FAQ to see if your question is covered. If not, we’re always looking for new problems to solve! Email yours to mac911@macworld.com, including screen captures as appropriate and whether you want your full name used. Not every question will be answered, we don’t reply to email, and we cannot provide direct troubleshooting advice.
[ad_2]
Source link