What happens when you trigger a car’s automated emergency stopping?
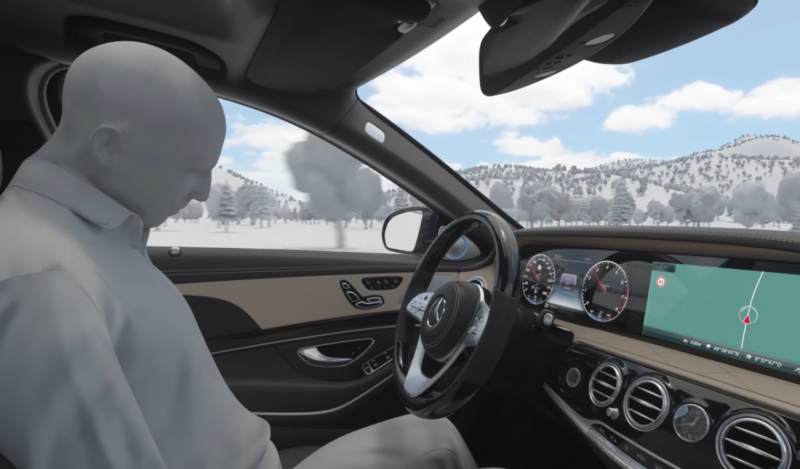

Enlarge (credit: Mercedes-Benz)
Most car accidents begin and end in a few seconds. That’s plenty of time to get in a tiny micro-nap while driving. The famous asleep-at-the-wheel film scene in National Lampoon’s Vacation, where Clark Griswold goes off to slumberland for 72 seconds while piloting the Wagon Queen Family Truckster (a paragon of automotive virtue but lacking any advanced driver safety systems), might be a comical look at this prospect. But if Clark were in the real world, he and his family would likely have been injured or killed—or they could have caused similar un-funny consequences for other motorists or pedestrians.
There’s plenty of real-world news on the topic right now. Early in 2023, the Automobile Association of America’s Foundation for Traffic Safety published a study estimating that 16–21 percent of all fatal vehicle crashes reported to police involve drowsy driving.
With the road fatality numbers in the US hovering close to 38,000 over the past few years, that means between 6,080 and 7,980 road deaths are linked to drowsy drivers. Further research by the AAA’s Foundation finds that drivers likely under-report drowsiness in all car crashes. Nodding off while driving is as dangerous as—and potentially more dangerous than—driving drunk. And while drunk-driving figures have decreased between 1991 and 2021, the opposite is true for drowsy driving.