Study: Scribes in ancient Egypt had really poor posture during work
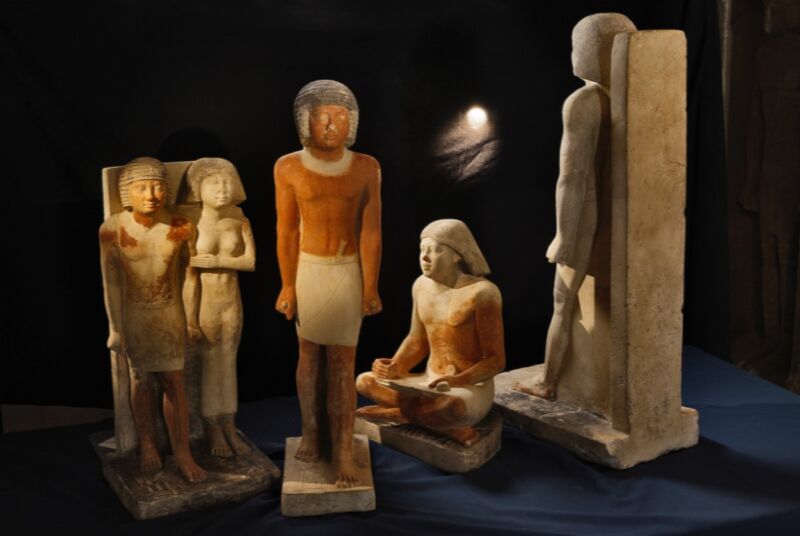

Enlarge / Statues depicting the high dignitary Nefer and his wife (Abusir, Egypt). (credit: Martin Frouz/Czech Institute of Egyptology/Charles University.)
Repetitive stress injuries are a common feature of modern life, especially for office workers who spend a good chunk of their working days at a desk typing on a computer. Apparently, scribes in ancient Egypt suffered from their own distinctive repetitive stress injuries, according to a new paper published in the journal Scientific Reports that provides fresh insights into how these scribes lived and worked during the third millennium BCE.
Egyptian kings, royal family members, and other elite people from this Fifth Dynasty era were buried in tombs in the acropolis at Abusir rather than at neighboring Giza, which by then had largely filled up thanks to all the activity during the Fourth Dynasty. The Czech Institute of Egyptology at Charles University in Prague has been conducting research at the site since 1960, leading to the discovery of nearly 200 tombs dating back to the Old Kingdom (between 2700 and 2180 BCE). The first human skeletons were excavated in 1976, and there are currently 221 Old Kingdom skeletons in the collection, 102 of which are male.
Scientists started looking into the health status and markers for specific activities in 2009, but it wasn’t until quite recently that there were enough skeletons to conduct a comprehensive study. That’s what Petra Brukner Havelková of Charles University and the National Museum in Prague, Czech Republic, and colleagues set out to do, analyzing the remains of 69 adult males of different social status and different ages at which they died.