Changing Paintings: 34 Minos and the Myrmidons

With Medea finally consigned to oblivion and Theseus united with his father, King Aegeus of Athens, Ovid’s Metamorphoses rushes on to a little-known group of myths explaining the origins of Minos and the fearsome Myrmidons who were later to fight for Achilles in the war against Troy.
The delight of King Aegeus in meeting his son at last proved short-lived when King Minos of Crete threatened war against Athens. Minos assembled a fleet of ships, and cruised the islands obtaining the allegiance and support of the small kingdoms there. When his fleet came to the island of Aegina, Aeacus its king refused on the grounds of his binding treaties with Athens. As the Cretan fleet sailed, Cephalus arrived from Athens, and was told of Aeacus’ unfailing allegiance. However, he noticed that people and things had changed since his last visit to Aegina.
King Aeacus then takes over the narration, giving his account of the plague that had almost destroyed the people of Aegina. It had arisen because of one of Jupiter’s extramarital affairs, with the nymph of the island, inevitably also named Aegina; Juno’s jealous reprisal against the nymph was largely expressed in a plague sent against the people of the island. Aeacus gives a vivid account of the deadly consequences of an infectious disease which sounds much like one of the many outbreaks of the plague that have struck Europe. In the end, with corpses being piled high unburied or in funeral pyres, Aeacus called on Jupiter either to give him his people back, or to kill him.
Aeacus saw an army of ants hard at work on a sacred oak tree, and asked that Jupiter give him such an army of people. When he slept that night, the king dreamed of those ants being transformed into people. The following morning, his son Telamon woke him, to tell him that overnight the city had been peopled afresh. They hailed Aeacus as king, and immediately went on to labour hard on the land and to become the fearsome band of warriors known as Myrmidons, a name derived from the Greek for ant, μύρμηξ (myrmex).
Later legend tells that the Myrmidons moved to Thessaly, from where Aeacus’ grandson Achilles took them with him to the Trojan War. The word has even entered the English language, although little-used for over a century. It came to mean a loyal and unquestioning follower, much like a worker ant.
Virgil Solis (1514–1562), Myrmidons (1581), engraving for Ovid’s Metamorphoses Book VII, 622-642, fol. 94 v., imago 11, location not known. Wikimedia Commons.
The first work of visual art which shows the Myrmidons seems to be Virgil Solis’s engraving for a 1581 edition of Metamorphoses. King Aeacus is shown calling on Jupiter to repopulate the island, as the ants climb the old oak tree, and babies spill out from a cleft in its trunk.
Jean-Michel Moreau le Jeune (1741-1814) Telemon and Aeacus (date not known), further details not known. Wikimedia Commons.
That was followed in the latter half of the eighteenth century by this engraving by Jean-Michel Moreau le Jeune, Telemon and Aeacus, showing Telemon taking his father Aeacus out to see the loyal and hard-working Myrmidons at the end of the story. I suspect that this too was made for an illustrated edition of Metamorphoses.
If Aeacus did not make sufficient impression on artists, the figure of Minos did, particularly as he, together with Aeacus and Rhadamanthus, was made a judge of the dead in Hades, after his death.
Michelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni (1475-1564), The Last Judgment (1537-41), fresco, Cappella Sistina, The Vatican. Wikimedia Commons.
Michelangelo shows Minos in that (Christianised) role in his huge fresco The Last Judgment (1537-41), with his attribute of a snake, which appears to be about to do Minos something of a mischief.
Minos also features in Dante’s Divine Comedy, which brought him to the attention of two of the greatest illustrators (and fine artists) of the nineteenth century, William Blake and Gustave Doré.
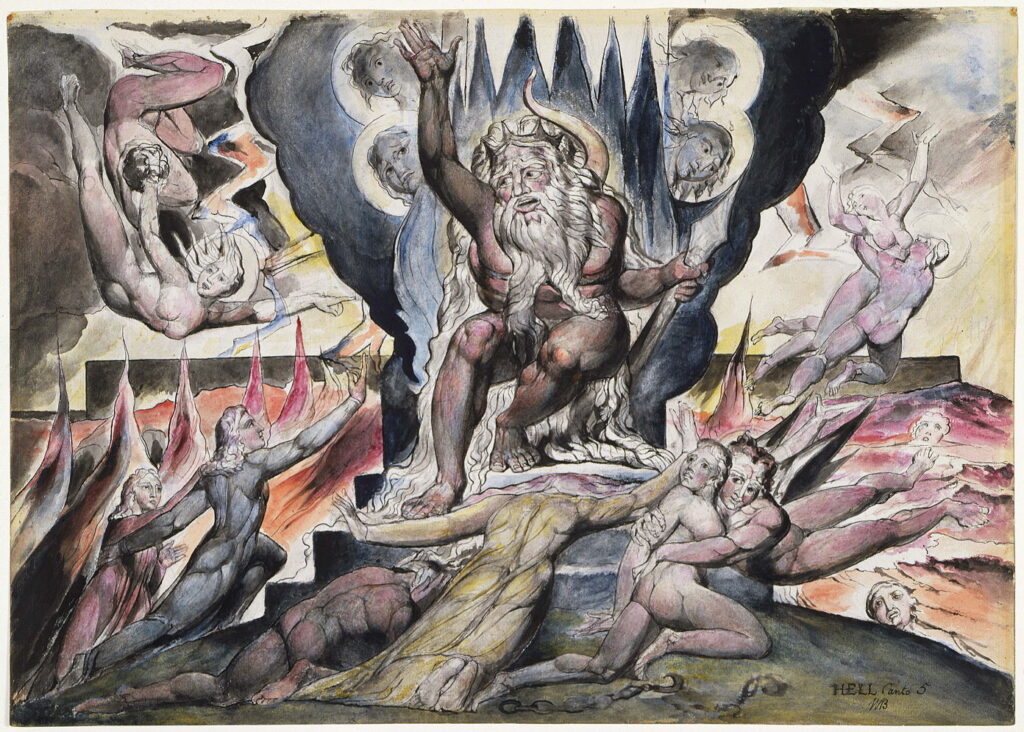
William Blake (1757–1827), Minos (1824-27), illustration to Dante’s “Divine Comedy”, watercolour on paper, dimensions not known, National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne, Australia. Wikimedia Commons.
Blake’s watercolour of Minos (1824-27) shows him presiding in judgement over four cavorting couples, in a thoroughly radical vision.
Gustave Doré (1832-1883), Minos, Judge of the Inferno (c 1861), illustration to Dante’s “Divine Comedy”, engraved by Gaston Monvoisin, further details not known. Image by Moïra Elliott, via Wikimedia Commons.
Doré’s version, engraved here by Gaston Monvoisin, is more restrained, and shows Minos’ trademark serpent. Below him are souls queued up for his judgement.