Reading visual art: 153 Catasterisation and assumption

In yesterday’s article, I showed examples of apotheoses. Following a couple of even more liberal interpretations, this article moves on to the second and third items in this list:
Apotheosis, when a pre-christian hero is elevated to the status of god or goddess;
Catasterisation, when a mortal is changed into a celestial body such as a star or constellation;
Assumption, when the Virgin Mary was taken up into Heaven;
Ascension, when Jesus Christ ascended into Heaven, and sometimes available to saints on their martyrdom.
Anne-Louis Girodet de Roussy-Trioson (1767–1824) (attr), Apotheosis of the French Heroes Who Died for the Fatherland during the War of Liberation, Ossian receiving the Ghosts of the French Heroes (c 1801), oil on canvas, 192 x 182 cm, Musée national des châteaux de Malmaison et de Bois-Préau, Paris. Wikimedia Commons.
Girodet’s painting of the Apotheosis of the French Heroes Who Died for the Fatherland during the War of Liberation, Ossian receiving the Ghosts of the French Heroes was probably completed in 1802, and is perhaps the most elaborate and complex painting inspired by the bogus Scottish poet Ossian. It’s unclear how those French war heroes became involved with Ossian, but an extraordinary mixture of myths and legends from contrasting cultures.
Vasily Vereshchagin (1842–1904), The Apotheosis of War (1871), oil on canvas, 127 x 197 cm, Tretyakov Gallery Государственная Третьяковская галерея, Moscow, Russia. Wikimedia Commons.
In Vasily Vereshchagin’s bleak Apotheosis of War (1871), ravens/crows perch on a huge pile of human skulls in a barren landscape outside the ruins of a town.
A few Christian religious paintings came close to being apotheoses.
Alexandre Cabanel (1823–1889), The Death of Moses (1850), oil on canvas, 140 x 204 cm, Musée Fabre, Montpellier, France. Wikimedia Commons.
Alexandre Cabanel’s The Death of Moses (1850) tackles one of the vaguer episodes in the life of this Old Testament prophet. When he was 120 years old, according to the book of Numbers, Moses assembled the tribes of Israel on the banks of the River Jordan, reminded them of the laws under which they must live, sang a song of praise, blessed the people, and passed his authority to Joshua. He then ascended Mount Nebo, looked over the Promised Land, and died. Cabanel shows this as an apotheosis, with God the Father (upper left) welcoming Moses (centre right) with open arms.
Being transformed into a celestial body in catasterisation was an honour accorded those mortals who couldn’t aspire to deity, among them the giant Orion. He arrived at Chios, where he became drunk, and raped Merope, the daughter of Oenopion. As punishment for that, Oenopion blinded Orion and cast him from his land. Orion then went to Lemnos, where Hephaistos took pity on him, and lent him his servant Kedalion to sit astride his shoulders and act as his guide. An oracle advised Orion to proceed east into the rays of the rising sun, so that those rays would restore his sight. So cured, Orion then went to Crete to hunt.
There are differing accounts of Orion’s death. Some involve his love affair with Eos, which was opposed (possibly out of jealousy) by Artemis. In these, Artemis ended up killing Orion with her arrows. Other versions claim he was killed by a giant scorpion. In death, Artemis asked that Zeus catasterised him, together with the scorpion, to form the constellation Scorpio. Once there, Orion pursues the daughters known as the Pleiades, which form a prominent open star cluster nearby.
Nicolas Poussin (1594–1665), Landscape with Orion, Blind Orion Searching for the Rising Sun (1658), oil on canvas, 119.1 × 182.9 cm, Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York, NY. Wikimedia Commons.
Poussin’s Landscape with Orion, or Blind Orion Searching for the Rising Sun was painted late in his career, in 1658, at a time when the artist’s hands were suffering a tremor that was starting to disrupt his ability to paint. It is among his finest allegorical landscapes, and one of the most intensely studied works of his career.
Set in one of Poussin’s wonderful idealised landscapes, near the coast, the giant Orion is striding purposefully towards the rising sun. He carries a huge hunting bow, and a quiver taller than a man. Standing on his shoulders is Kedalion, servant to Hephaistos, who is acting as his guide. Above and beyond Orion is a strange formation of backlit cloud, generally interpreted as being storm-cloud. Atop that is the standing figure of Artemis, with her distinctive crescent moon coronet, and an owl perched on her left shoulder. She leans nonchalantly against the cloud, her head propped against her right hand. In the far distance is the sea, with a prominent lighthouse.
Daniel Seiter ( –1705), Diana by the Corpse of Orion (1685), 116 × 152 cm, Musée du Louvre, Paris. Image by Musée du Louvre/A. Dequier – M. Bard, via Wikimedia Commons.
There have been few other attempts to tell any part of the story of Orion on canvas. In 1685, Daniel Seiter ( –1705) painted this view of Diana by the Corpse of Orion, following in the brushstrokes of his teacher Johann Carl Loth. This shows Diana (Artemis), with her distinctive crescent moon, looking regretfully at the dead Orion, after she had killed him with her arrows.
Sidney Hall (1788–1831), Orion (1825), etching, hand-coloured, plate 29 in Urania’s Mirror, set of celestial cards, location not known. Restoration by Adam Cuerden, via Wikimedia Commons.
Sidney Hall’s etching of Orion, a hand-coloured plate in a set of celestial cards from 1825, is an ingenious lesson in observational astronomy.
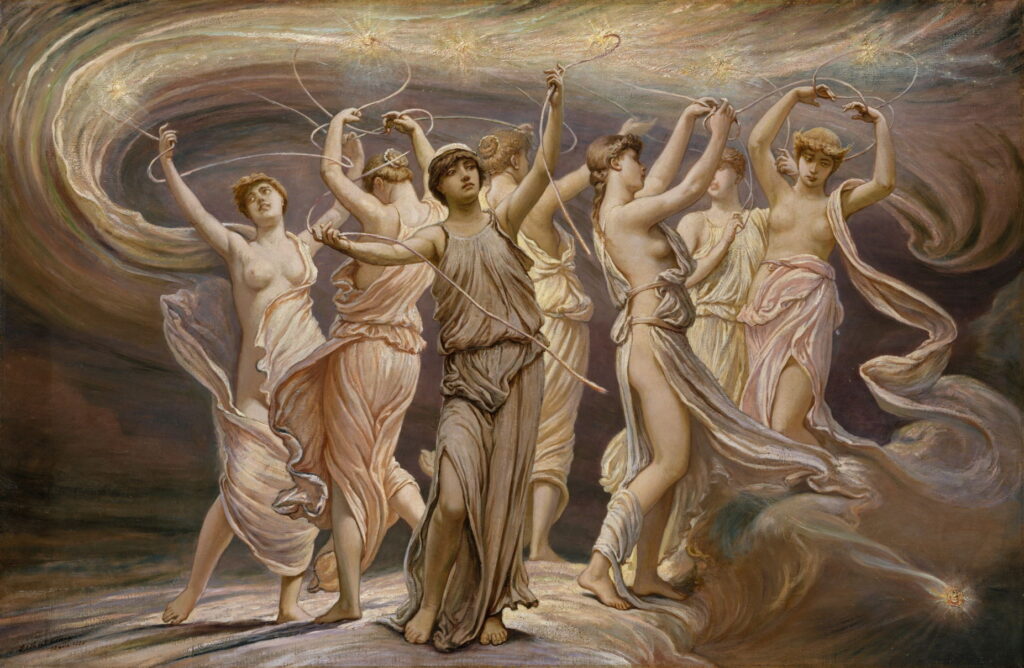
The Pleiades were originally the seven daughters of the titan Atlas and the sea-nymph Pleione. When Atlas was made to carry the heavens on his shoulders, Orion started to pursue the Pleiades, so Zeus transformed them first into doves, then into stars. Their name is given to a star cluster, which appears to be chased across the night sky by the constellation of Orion.
Elihu Vedder (1836–1923), The Pleiades (1885), oil on canvas, 61.3 × 95.6 cm, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York, NY. Wikimedia Commons.
Elihu Vedder’s painting of The Pleiades (1885) was made in association with his first illustration for the Rubaiyat of Omar Khayyam, representing Khayyam’s horoscope. Each of the sisters is connected by a thread to their corresponding star, perhaps representing the process of catasterisation.
There are a great many paintings of the Assumption of the Virgin Mary, of which I show here just a tiny sample.
Francesco Botticini (1446–1498), Assumption of the Virgin (c 1475-76), tempera on wood, 228.6 x 377.2 cm, The National Gallery, London. Wikimedia Commons.
Francesco Botticini’s spectacular example painted in about 1475-76 places unusual emphasis on Paradise, with its triple tiers of figures rising to those of the Virgin Mary kneeling in front of Christ at its summit.
Jacopo Tintoretto (c 1518-1594), The Assumption of The Virgin (E&I 91) (c 1563), oil on canvas, 440 x 260 cm, Cappella di Santa Maria Assunta, Gesuiti, Venice, Italy. Image by Didier Descouens, via Wikimedia Commons.
Tintoretto painted several versions of The Assumption of The Virgin, this one for the Cappella di Santa Maria Assunta, in the Gesuiti, Venice. It’s thought that Tintoretto had promised to paint this in the style of Veronese.
Nicolas Poussin (1594–1665), The Assumption of the Virgin (c 1650), oil on canvas, 57 x 40 cm, Musée du Louvre, Paris. Wikimedia Commons.
Poussin’s Assumption of the Virgin from about 1650 is plainer and more orthodox.
Gaetano Previati (1852–1920), Assumption (c 1901-03), oil on canvas, 105 x 87 cm, Museo dell’Ottocento, Ferrara, Italy. Image by Nicola Quirico, via Wikimedia Commons.
Gaetano Previati’s Divisionist rendering of the Assumption from about 1901-03 shows a group of winged angels raising Mary’s body to Heaven.