The Real Country: 4 Gleaning

Once a cereal crop had been harvested and gathered for threshing, the fields might then be scavenged for any remaining grain, a process known as gleaning. Although this has been described since Old Testament times, there’s uncertainty as to who gleaned, and where they were able to glean. This article shows a selection of paintings from the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries showing gleaning, to see if they cast further light on those questions.
Biblical accounts establish that gleaning was then a means for the poorest in society to acquire their own free supply of grain, and was a right of the poor. Some assume that the same practice continued, under the same right, until it fell into disuse in the late twentieth century. That ignores complex changes in land ownership and rights, and national law, and makes assumptions about rural economies that may not be correct.
The majority of those living in the country between 1500 and 1800 had little need for money. Almost everything they required in life was grown or made locally, and there were few if any consumer goods that they would need to purchase. Most lived in two sets of clothes: working dress, which was handed down, patched and repaired until it was unwearable, and a Sunday outfit worn when attending church, similarly inherited. Furniture was scant, made from local wood, and handed down through generations. Food and other goods that the family couldn’t supply itself would normally be obtained by barter with a neighbour. While those with more land and animals could sell them at market, and use the proceeds to buy luxuries, that remained out of the reach of the majority. It appears to have been that majority who gleaned the fields after harvest.
Although some countries in Europe retained gleaning rights on the strength of Biblical law, as land was enclosed and brought into increasingly complex systems of private ownership and rights, some land owners challenged that ancient right, and in 1788 a notable English legal case set the precedent that there was no universal right to glean, no matter how poor you might be. Nevertheless, many landowners continued to allow gleaning on their land, and in some areas these were celebrated alongside the harvest itself. Gleaning, like much else in the country, thus varied from country to country, and by region and village, but wasn’t confined to the poorest by any means.
One pitfall in looking at paintings of gleaning is that some are retelling the Biblical story of Ruth and Boaz, rather than depicting contemporary gleaning.
Samuel Palmer (1805–1881), The Gleaning Field (c 1833), tempera on mahogany, 30.5 x 45.4 cm, The Tate Gallery (Bequeathed by Mrs Louisa Mary Garrett 1936), London. © The Tate Gallery and Photographic Rights © Tate (2016), CC-BY-NC-ND 3.0 (Unported), http://www.tate.org.uk/art/artworks/palmer-the-gleaning-field-n04842
In Samuel Palmer’s The Gleaning Field (c 1833), as in other accounts, gleaners appear to have been mostly women.
Jules Breton (1827–1906), The Gleaners (1854), oil on canvas, 93 × 138 cm, The National Gallery of Ireland/Gailearaí Náisiúnta na hÉireann, Dublin, Ireland. The Athenaeum.
In 1854, Jules Breton returned to live in his home village of Courrières, not far from Calais in north-east France, and started painting agricultural workers in the local landscape. His style changed dramatically, and the following year he enjoyed success with his first masterpiece, The Gleaners (1854), which won him a third-class medal at the 1855 Paris Salon. Overseeing this gleaning is the garde champêtre or village policeman, an older man distinguished by his official hat and armband, who was probably an army veteran. In the background, behind the grainstacks that were later to be such popular motifs for the Impressionists, is the village church tower, surrounded by its houses.
Breton had started to plan this painting soon after his return. He made a series of studies, several of which survive, for its figures, but the view appears to be faithful to reality. The figure of the young woman walking across the view from the right (in front of the garde champêtre) seems to have been modelled on the daughter of Breton’s first art teacher, whom the artist married in 1858.
Jean-François Millet (1814–1875), The Gleaners (1857), oil on canvas, 83.5 × 110 cm, Musée d’Orsay, Paris. Wikimedia Commons.
Jean-François Millet’s hope for the Salon two years later was his substantial painting of The Gleaners (1857), which is completely different in concept. The distant wagon, grainstacks, and village may appear common elements, as are the three women bent over to glean in the foreground, but that is as far as the similarities go.
Millet’s composition is sparse, concentrating on those three figures. There are no distractions, such as the garde champêtre to add colour or humour: it’s all about poverty, and smacked of socialism; unlike Breton’s painting it got the thumbs-down from both the rich and the middle classes who frequented the Salon. Millet had also been born and brought up in the country, in his case further west on the north coast of France, in the Normandy village of Gruchy, where he had worked on the land.
Jules Breton (1827–1906), Calling in the Gleaners (1859), oil on canvas, 90 x 176 cm, Musée d’Orsay, Paris. Wikimedia Commons.
Breton’s Calling in the Gleaners (also known as The Recall of the Gleaners, Artois) (1859) is one of the treasures of the Musée d’Orsay. With the light now fading, and the first thin crescent of the waxing moon in the sky, the loose flock of weary women and children make their way back home with their hard-won wheat. At the far left, the garde champêtre calls the last in, so that he can go home for the night. Behind them a flock of sheep is grazing on the adjacent pasture.
Eugène Burnand (1850–1921), Gleaners (1880), oil, dimensions not known, musée Eugène Burnand, Moudon, Switzerland. Wikimedia Commons.
Painted in 1880, Eugène Burnand’s Gleaners are set in high Alpine meadows, two girls with meagre gleanings. They are dressed in plain working clothes, but don’t appear particularly poor. Behind them a cart carries away the main harvest.
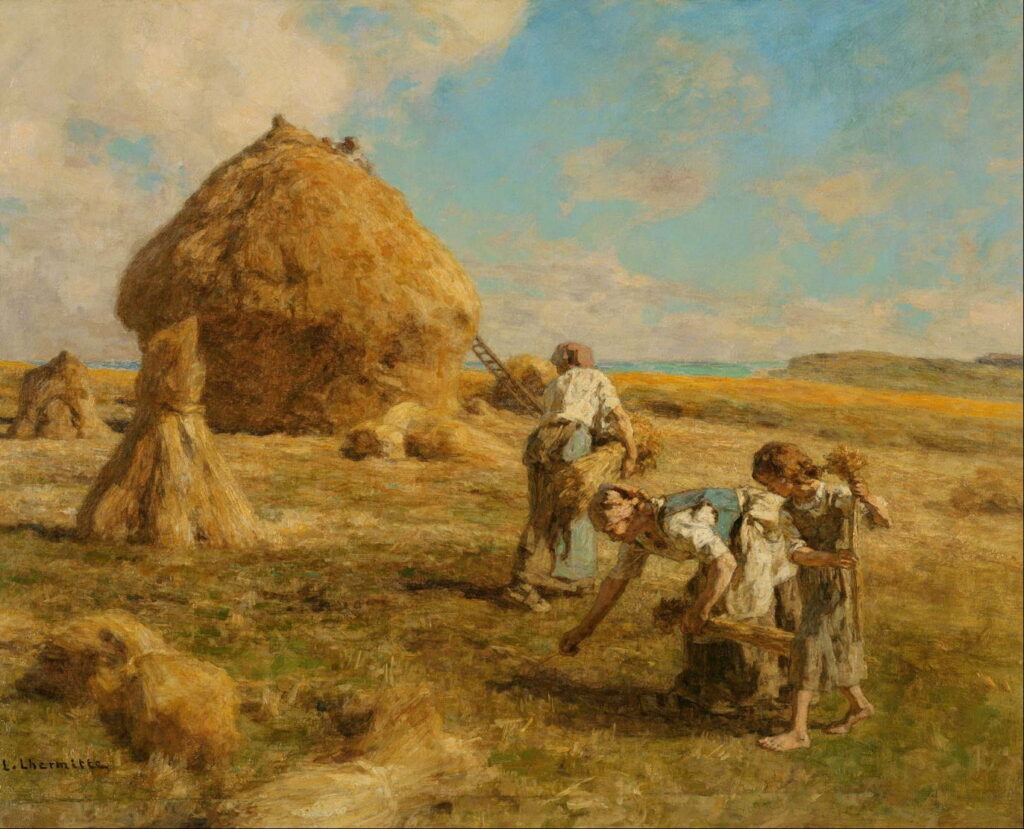
Léon Augustin Lhermitte (1844–1925), Gleaners (1887), oil on canvas, dimensions not known, Philadelphia Museum of Art, Philadelphia, PA. Wikimedia Commons.
Léon Augustin Lhermitte’s most enduring expression of rural poverty was in showing four women salvaging the remains left in the fields after the harvest: the Gleaners, here his version of 1887. Lhermitte was another son of the country, this time Mont-Saint-Père in Picardy, inland in north-east France, although his father was a schoolteacher.
Hans Andersen Brendekilde (1857–1942), Cowed (1887), media not known, 126 x 152.3 cm, Fyns Kunstmuseum, Odense, Denmark. Wikimedia Commons.
Cowed from 1887 shows gleaners at work in a field after the harvest in Denmark, but there’s much more to Hans Andersen Brendekilde’s story than that. The owner of the large farm in the left distance has gathered in their grain, and their harvesters have been paid off for their effort. Then out come the gleaners to scavenge what they can from the fields.
The family group in front of us consists of three generations: mother is still bent over, hard at work gleaning her handful of corn. Her husband is taking a short break, sitting on the sack in his large blue wooden clogs. Stood looking at him is their daughter, engaged in a serious conversation with her father, as her young child plays on the ground.
The daughter is finely dressed under her coarse gleaning apron, and wears a hat more appropriate to someone in service as a maid, or similar, in a rich household in the nearby town. She looks anxious and flushed, and is almost certainly an unmarried mother, abandoned by her young child’s father, and it’s surely she who is oppressed or ‘cowed’. Their difficult family discussion is being watched by another young woman at the far left, who might be a younger sister, perhaps.
Brendekilde took his name from the small village of Brændekilde, near Odense on the island of Funen in Denmark. The son of a clog maker, he lived with his grandparents for several years when a child, and at the age of ten made his living as a shepherd.
Camille Pissarro (1830-1903), The Gleaners (1889), oil on canvas, 65.5 x 81 cm, Kunstmuseum, Basel, Switzerland. WikiArt.
The Impressionists seldom seem to have painted controversial social issues. One of the few exceptions to this proved a lesson for Camille Pissarro in the practicality of Divisionism. He started work on his intensely sensory and idyllic painting The Gleaners in early 1888, using a squared-up study in gouache to finalise his composition. He found the painting hard, and wrote that he needed models so that he could complete its detail, which did the following year.
As Europe moved into the twentieth century, gleaning became increasingly unreal and romantic.
Sir George Clausen (1852–1944), Gleaners Coming Home (1904), oil on canvas, 92.7 x 122.6 cm, The Tate Gallery (Presented by C.N. Luxmoore 1929), London. Photographic Rights © Tate 2016, CC-BY-NC-ND 3.0 (Unported), http://www.tate.org.uk/art/artworks/clausen-gleaners-coming-home-n04486
Gleaners were still commonplace in the Essex grain fields at harvest time, trying to scrape enough waste grain from the ground to feed their families. In Sir George Clausen’s Gleaners Coming Home from 1904, swirling brushstrokes make the gleaners’ improbably smart clothes appear to move as they walk home in the evening sunlight.
Sir George Clausen (1852–1944), The Gleaners Returning (1908), oil on canvas, 83.8 x 66.0 cm, The Tate Gallery (Presented by the Trustees of the Chantrey Bequest 1908), London. Photographic Rights © Tate 2016, CC-BY-NC-ND 3.0 (Unported), http://www.tate.org.uk/art/artworks/clausen-the-gleaners-returning-n02259
Clausen’s The Gleaners Returning (1908) is a marvellous contre-jour (into the light) view, again with swirling brushstrokes imparting movement in the women’s clothes, and no hint of their poverty.
Léon Augustin Lhermitte (1844–1925), Gleaners Near Haystacks (1912), oil on canvas, 89.5 × 128.9 cm, Private collection. Wikimedia Commons.
Lhermitte’s Gleaners Near Haystacks (1912) shows a group of women gleaning, two of them almost bent double.
Léon Augustin Lhermitte (1844–1925), Gleaning Women (1920), oil on canvas, 65.4 x 81.2 cm, National Museum of Western Art 国立西洋美術館 (Kokuritsu seiyō bijutsukan), Tokyo, Japan. Wikimedia Commons.
Even when he was well into his seventies, Lhermitte seemed able to find time and energy for just another painting of gleaners, in his Gleaning Women of 1920.
With the increasing depopulation of Europe’s rural areas and the introduction of mechanical methods of harvesting, gleaning seems to have died out by the middle of the twentieth century, only to reappear around 2000. It’s now an organised voluntary activity arranged with farmers, to recover crops unsuitable for mechanical harvesting, and other recoverable sources.
As with many other aspects of rural life, gleaning appears to have varied according to era and location. In some areas it seems to have been confined to those who were struggling to provide sufficient food for themselves, in the Biblical tradition. In others it was more general, and a normal phase of the harvest supplying most families with a free top-up of grain they could get ground by a miller to add to their supply of bread in the coming winter. It could also yield substantial amounts of grain: one report claims a widow and her three sons gleaned 325 kg (720 pounds) of wheat from one harvest. After all, if left in the field where it was, it would only have been ploughed back into the ground later in the autumn, and gone to waste.
Reference
David Hoseason Morgan (1982) Harvesters and Harvesting 1840-1900, Routledge ISBN 978 1 138 74476 9.