Changing Paintings: 38 The Calydonian Boar Hunt

As Ovid approaches the midpoint of Book 8 of his Metamorphoses, he has just left Daedalus burying his son Icarus after their flight from Crete went tragically wrong. He then relates one of the greatest stories of the period, of the Calydonian Boar Hunt, which he tells with wry humour, lightening its gruesome events.
With the Minotaur dead, and Daedalus welcomed to Sicily, Theseus was sought to bring help to Calydon, a city in southern Greece that was being plagued by a wild boar as big as an ox, the vengeance of Diana. Calydon’s king Oeneus had paid oblations to most of the deities, but not to Diana, so incurring her wrath. Ovid provides a vivid description of how the beast was destroying crops and livestock in the area surrounding the city.
A long list of heroes were summoned to hunt the boar: Theseus brought Pirithous with him, Telamon the son of King Aeacus came, Meleager from Calydon itself, and more than a dozen others. With them came a plainly dressed young woman, Atalanta, to whom Meleager took an immediate fancy.
Nicolas Poussin (1594–1665) (attr), The Hunt of Meleager and Atalanta (Depart for the Hunt) (c 1634-39), oil on canvas, 160 x 360 cm, Museo Nacional del Prado, Madrid. Wikimedia Commons.
Their departure is shown in The Hunt of Meleager and Atalanta (c 1634-39), dubiously attributed to Nicolas Poussin. The procession of heroes, some on horseback, others on foot, makes its way out into the Calydonian countryside. It’s easy to spot Atalanta who is wearing a plain blue robe, holding her bow, and riding a white horse, towards the right. There are two statues behind: on the right is Pan with his pipes, and in the centre is Diana, cause of the problem, with the skull of a boar shown on the tree behind.
The hunters travelled to dense ancient woodland to trap the boar, where they laid their nets, released their dogs, and set about trying to track their quarry. They found the boar at the boggy bottom of a deep gully, from where he rushed at them. Several threw their javelins, but none hit the beast, who promptly charged at the men, goring several of them fatally before disappearing into a dense thicket.
Telamon tripped over in his pursuit, and as he was being helped up, Atalanta loosed an arrow that grazed the boar’s back and buried itself into the animal’s head just below the ear. Meleager praised her for this first success.
Ancaeus then boasted how his weapons would surpass those of any woman, and raised himself to bring his double axe down on the boar. The beast gored and disembowelled him before he could strike. Pirithous threw his spear only to strike the branch of a chestnut tree, and Jason’s javelin impaled one of their dogs, pinning it to the ground.
At this stage, the efforts of the heroes had been at best amateur, if not farcical. It was now up to Meleager, whose second spear-shot struck home in the boar’s back, allowing him to finish the beast off.
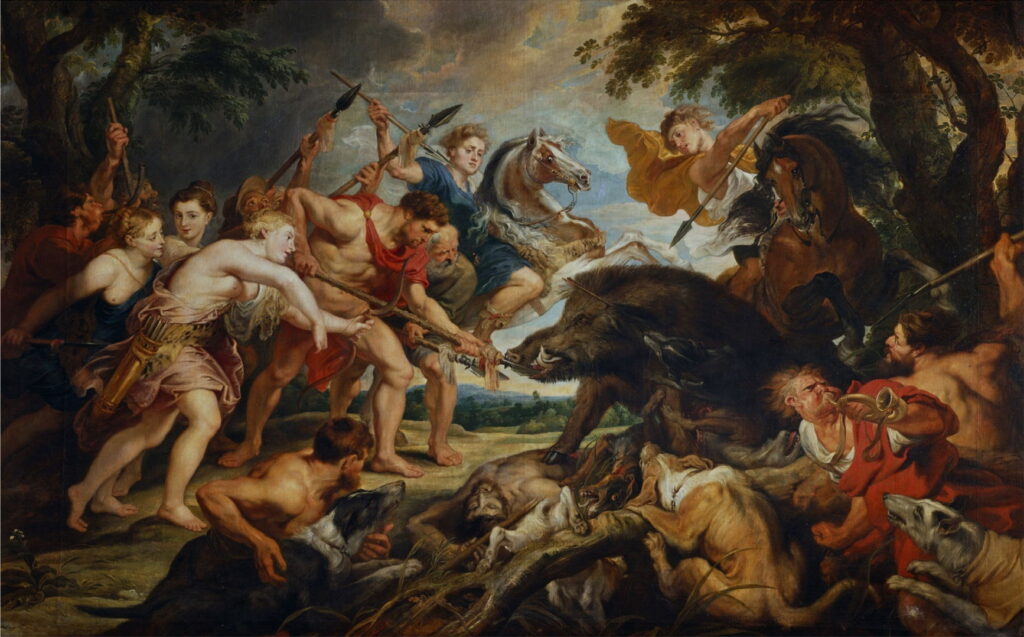
Peter Paul Rubens (1577–1640), The Calydonian Boar Hunt (c 1611-12), oil on panel, 59.2 × 89.7 cm, J. Paul Getty Museum, Los Angeles, CA. Wikimedia Commons.
Peter Paul Rubens and his workshop painted several different accounts. The first appears to have been The Calydonian Boar Hunt, in about 1611-12, now in the Getty. Here Meleager is just about to finish the wounded boar off. Atalanta’s arrow is visible by its left ear, and the body of Ancaeus lies just behind Meleager’s left foot. The wall of horses behind the boar, and the crowd of hunters behind Meleager, including Atalanta in blue, frame the combatants in the foreground, with some spears directing the gaze at a visual centre of the boar’s snout.
Peter Paul Rubens (1577–1640), Meleager and Atalanta and the Hunt of the Calydonian Boar (study) (c 1618-19), oil on panel, 47.6 × 74 cm, Norton Simon Museum, Pasadena, CA. Wikimedia Commons.
A few years later, in about 1618-19, Rubens reworked his composition in this marvellous study of Meleager and Atalanta and the Hunt of the Calydonian Boar. This shifts the visual centre closer to the geometric centre, and brings the gaze in using a greater range of radials. It also gives Atalanta a more active part, as in Ovid’s text.
Peter Paul Rubens (1577–1640), The Hunt of Meleager and Atalanta (c 1616-20), oil on canvas, 257 × 416 cm, Kunsthistorisches Museum, Vienna, Austria. Wikimedia Commons.
Rubens’ finished result is The Hunt of Meleager and Atalanta probably from around 1618-20, now in Vienna. Meleager has aged slightly, and the boar rests its hoof on the body of Ancaeus. Radial lines of spears are augmented by a dog and some human figures, and the centre of the painting now includes a landscape, with bright sky used to emphasise the visual centre. It also seems to show not just Atalanta at the right hand of Meleager, but two other women behind her, and possibly another in blue robes on a horse just above the middle of the painting.
Meleager stood, one foot on the boar’s head, and gave his prize to Atalanta, to share the glory with him: he delighted her by giving the young woman the boar’s skin and head with its tusks as large as an elephant’s. But the two sons of Thestius objected to this, and took Meleager’s gift, enraging him, who promptly killed them both with his sword, leading into the next story.
Jacob Jordaens (1593–1678), Meleager and Atalanta (1620-50), oil on canvas, 152.3 × 240.5 cm, Museo Nacional del Prado, Madrid. Wikimedia Commons.
With the boar now dead, Jacob Jordaens shows Meleager and Atalanta (1620-50) allocating the best part of the prize, the boar’s head. This is raised high above the couple at the right. On the left, though, the two sons of Thestius look incredulous, and are just about to refute Meleager, and take the head from Atalanta.
Peter Paul Rubens (1577–1640) and workshop, Meleager Presents Atalanta with the Head of the Calydonian Boar (before 1640), oil on panel, 76 x 57.5 cm, location not known. Wikimedia Commons.
Rubens and his workshop’s Meleager Presents Atalanta with the Head of the Calydonian Boar (before 1640) prefers a more private award by Meleager. The couple are here alone, apart from an inevitable winged cupid, and a goddess, most probably Diana, watching from the heavens. Meleager stands on the forelegs of the dead boar, and his spear behind is still covered in its blood.