Why Apple maxes out at two active SIM/eSIMs on its hardware
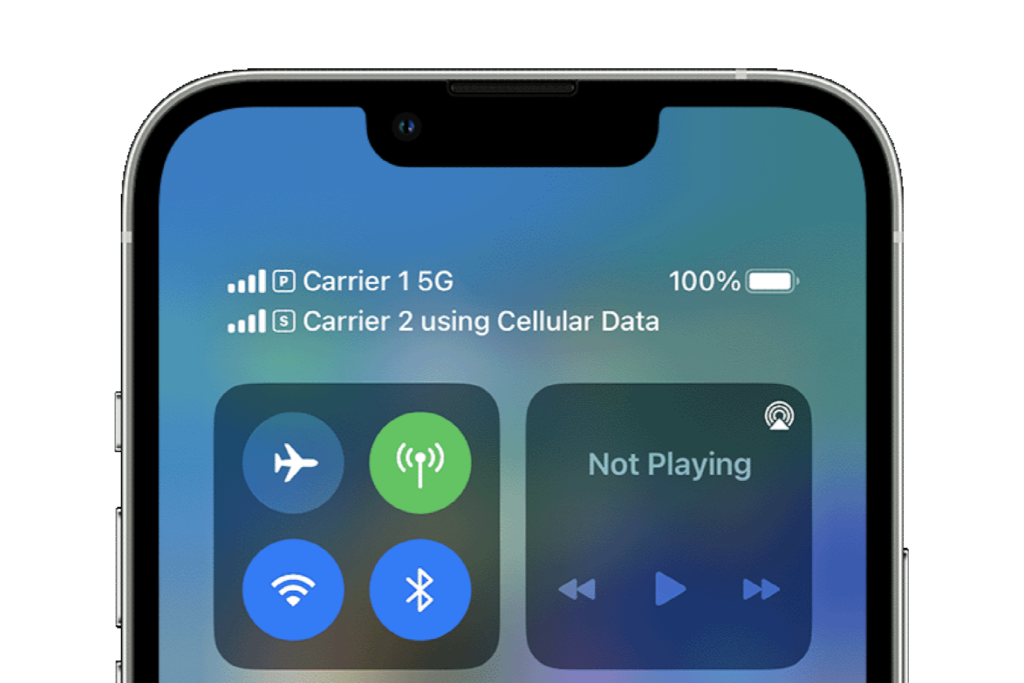
Why can’t you have three cellular network IDs on your iPhone or iPad active at once–two eSIMs and one SIM or three eSIMs? Or even more? You might think Apple is trying to frustrate you. But it’s a hardware limitation that’s designed around what Apple thinks represents the vast majority of its users’ needs.
The short answer is that Apple has the necessary hardware built into some iPads and iPhones could allow two (iPad) or three (iPhone) cellular subscriptions at once, but the architecture of those devices only allows one (iPad) or two (iPhone) to be in use at any given time. Newer U.S. models of iPhones have only the circuitry required to manage two active cellular subscriptions, not three, making it an entirely moot point.
Let’s dig into the details.
SIMpathy for the traveler
The SIM (Subscriber Identity Module) is a way for a device with cellular capability to identify itself to any compatible network nearby. It’s essentially an ID connected to a billing account. When a cellular phone, watch, or other device connects to a cell network base station, the SIM serves as a unique identifier that allows the operator of that base station to check for active service–all in a split second.
During the explosion of smartphones, the Mini SIM format was dominant and measured about 1 by 0.6 inches (25 by 15 mm). Most of that was a plastic surround to protect the circuitry. However, the form factor shrunk over several years to Nano, about 0.5 by 3.5 inches (12.3 by 8.8 mm)—otherwise known as “the size that when you drop it, it will slip into any crack and be lost forever.”
An eSIM (embedded not electronic SIM) does away with the packaging and the ability to remove it. But it’s still a SIM: an eSIM is circuitry built into a phone, tablet, watch, or other hardware that can load SIM information. It acts like and looks like a SIM to a cellular network. Apple and other companies use software to program the eSIM with subscriber information.
Due to high roaming costs, SIMs were a convenient way for travelers to cut costs by installing a SIM for a local service plan in the country or region they arrived in. A common task for many people upon entering a country other than their own was to find an airport kiosk or convenience store, purchase a SIM with a cheap plan, find a paperclip or SIM removal tool, and carefully swap out the SIM. You could eventually pre-purchase these SIMs, but I recall a very tedious time of swapping four Nano SIMs for my family on landing in London after 14 hours of flying.
The eSIM does away with the need to have a physical item. Using one of a few methods, the eSIM is loaded with the correct subscriber information and activated just like a SIM card. Apple began including an eSIM module with the iPhone XS, iPhone XS Max, and iPhone XR; the list of starting models for iPads with eSIMs has nine entries!
The limits on total SIMs
With a SIM/eSIM iPhone or iPad, you can activate the eSIM as the only cellular plan on your device. In Apple’s peculiar phrasing, you can install “eight or more” eSIMs–why not one or more if the company doesn’t specify the top limit?
An iPad can only have a single SIM or eSIM active, but you can use the Dual SIM feature starting with those iPhone models above with iOS 12.1 or later. To use 5G this way, you need an iPhone 12 series phone or later with iOS 14.5 or later installed.
The Dual SIM lets you activate a SIM and eSIM or, starting with the iPhone 13 series, either that or two eSIMs at once. Apple eliminated the SIM module from iPhones sold in the United States, starting with the iPhone 14 models.
Because an eSIM is a physical piece of hardware, the limitation on how many SIM/eSIMs you can use is physical, too, not an arbitrary software restriction:
On iPhones that support Dual SIMs with two eSIMs, Apple has two eSIM modules in the phones.
On iPhones that support a single SIM and one eSIM, Apple has the SIM card slot and a single eSIM module.
On an iPad that can handle a SIM or eSIM and on iPhones with the capability of a SIM/eSIM or dual eSIM option, Apple made a choice: it clearly built the hardware to route just one SIM signal, even though it could have had two (iPad) or three (iPhone).
For that last choice, I assume Apple didn’t think the extra cost of supporting a SIM plus two eSIMs made any sense for its user base, particularly since the company was already moving to reduce the cost of goods with its shift to eSIM-only iPhones in the United States.
Eventually, when eSIMs are supported by the vast majority of carriers (a point we’re nearing) Apple will certainly ditch the SIM slot on all iPhones and iPads worldwide just as it got rid of the headphone plug on iPhones years ago.
This Mac 911 article is in response to a question submitted by an anonymous Macworld reader.
Ask Mac 911
We’ve compiled a list of the questions we get asked most frequently, along with answers and links to columns: read our super FAQ to see if your question is covered. If not, we’re always looking for new problems to solve! Email yours to mac911@macworld.com, including screen captures as appropriate and whether you want your full name used. Not every question will be answered; we don’t reply to emails, and we cannot provide direct troubleshooting advice.



