Boccaccio’s Decameron: paintings of Cimon and Iphigenia

In the 650 years since Giovanni Boccaccio’s Decameron started to sweep across Europe, this collection of a hundred short stories has proved one of the most enduring works of literature. I have already given an account of its more painted passages, but this weekend I look in detail at two of them: today that of Cimon and Iphigenia, as told by Panfilo on the fifth day, and tomorrow the tragic tale of Lisabetta related by Filomena on the fourth.
Boccaccio was born in or near Florence in Italy in 1313. He became a scholar and writer based mainly in Florence, and might have been there when it was struck by the Black Death in 1348. The Decameron’s framing story describes that catastrophe, and how a group of seven young women were taking shelter in one of the city’s great churches. They fled as a group to the country nearby, in the company of some servants and three young men. Once settled in an abandoned mansion, the ten decided that one of the means they would use to pass their self-imposed exile was by telling one another stories. Over the next two weeks, each told one story every weekday, delivering the total of a hundred.
For the fifth day of these stories, Fiammetta chose the theme of the adventures of lovers who survived calamities or misfortunes and reached a state of happiness. The first of these is the story of Cimon (or Cymon) and Iphigenia told by Panfilo, which has probably been painted more than any other story in the whole of the Decameron, by masters from Rubens to Frederic, Lord Leighton. What’s most unusual is that every one of those paintings shows a single scene from the second page of a story that runs on for another ten pages, and develops a very different plot.
Cimon’s father was a wealthy Cypriot, but Cimon, a nickname given in honour of his apparent simplicity and uncouthness, was his problem child. He was exceedingly handsome and had a fine physique, but behaved as a complete imbecile. He appeared unable to learn anything, even basic manners, so was sent to live with the farm-workers on his father’s large estates.
One afternoon in May, Cimon was out walking when he reached a fountain in a clearing surrounded by tall trees. Lying asleep on the grass by that fountain was a beautiful young woman, Iphigenia, wearing a flimsy dress that left nothing to the imagination. Sleeping by her were her attendants, two women and a man. Cimon was immediately enraptured, leaned on his stick, and stared at her. As he did so, his simple mind started to change.
Master of the Campana Panels (dates not known), Cymon and Iphigenia (c 1525), tempera on panel, 58 x 170 cm, location not known. Wikimedia Commons.
As with many of Boccaccio’s stories, this is shown on a wedding cassone, here from about 1525. It’s relatively simple: there’s no sign of Iphigenia’s attendants, but there is a second image of Cimon walking along a path at the far right.
Peter Paul Rubens (1577–1640), Frans Snyders (1579–1657) and Jan Wildens (1584/86–1653), Cymon and Iphigenia (c 1617), oil on canvas, 208 × 282 cm, Kunsthistorisches Museum, Vienna, Austria. Wikimedia Commons.
In about 1617, Peter Paul Rubens joined talents with Frans Snyders (who painted the still life with monkeys at the lower right) and Jan Wildens (for its landscape background) in their marvellous Cymon and Iphigenia. This is accurate in its details too, with the correct quota of attendants, and a splendid fountain at the left. Cimon really does look like Boccaccio’s uncouth simpleton.
Willem Van Mieris (1662-1747), Cymon and Iphigenia (1698), oil on canvas, 27 x 34.8 cm, Museo Poldi Pezzoli, Milan, Italy. Wikimedia Commons.
Willem Van Mieris’ Cymon and Iphigenia from 1698 treats the scene more in the vein of Poussin or Claude, again remaining true to Boccaccio’s details.
Benjamin West (1738–1820), Cymon and Iphigenia (c 1766), oil on panel, 61.3 × 82.6 cm, Yale Center for British Art, New Haven, CT. Wikimedia Commons.
Benjamin West was more coy in both his depictions of this scene. His earlier Cymon and Iphigenia from about 1766 (above) was well-received at the time. Six years later, in 1773, he reversed the composition, and was even more restrained in the display of flesh, as shown below.
Benjamin West (1738–1820), Cymon and Iphigenia (1773), oil on canvas, 127 x 160.3 cm, Los Angeles County Museum of Art (LACMA), Los Angeles, CA. Wikimedia Commons.
Angelica Kauffman (1741–1807), Cymon and Iphigenia (c 1780), oil on canvas, diam 62.2 cm, Gibbes Museum of Art, Charleston, SC. Wikimedia Commons.
A few years later, in about 1780, Angelica Kauffman painted this delightful tondo of Cymon and Iphigenia, another variation on the same theme. The cultural contrast between the young man and woman isn’t as stark.
John Everett Millais (1829–1896), Cymon and Iphigenia (1848), oil on canvas, dimensions not known, Lady Lever Art Gallery, Liverpool, England. Wikimedia Commons.
When he was only eighteen, John Everett Millais painted what was to be his last work before he embraced Pre-Raphaelite style: Cymon and Iphigenia (1848). This bears less resemblance to Boccaccio’s story, which is to be expected as Millais didn’t use the Decameron as his literary reference, but a later re-telling by the English poet John Dryden, to which this is more faithful.
Frederic, Lord Leighton (1830-1896), Cymon and Iphigenia (study) (1884), oil on canvas, 43.1 x 66.2 cm, Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia. Wikimedia Commons.
In 1884, Frederic, Lord Leighton painted what I think remains the most luxuriant and sensuous treatment of this scene. This study shows Leighton confirming his composition and use of colour.
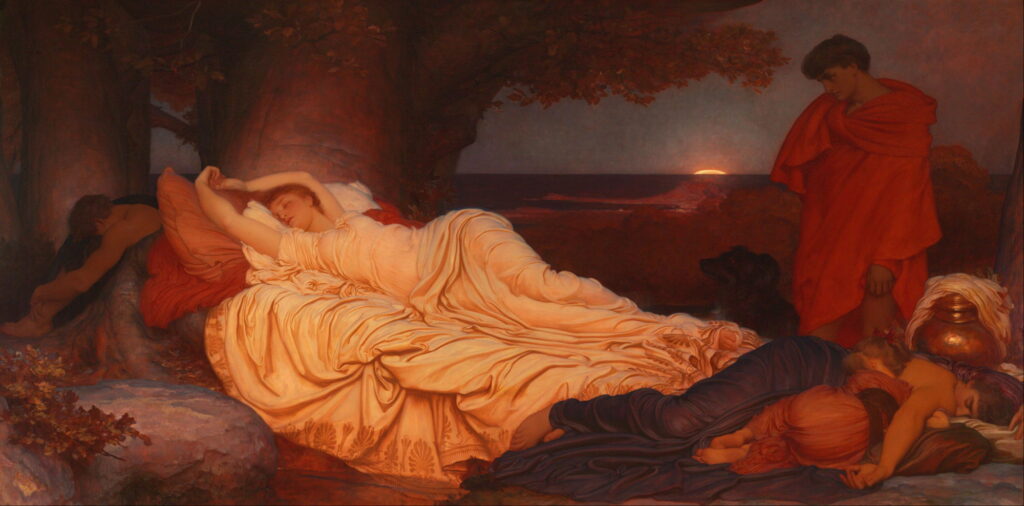
Frederic, Lord Leighton (1830-1896), Cymon and Iphigenia (1884), oil on canvas, 218.4 x 390 cm, Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia. Wikimedia Commons.
His finished painting, Cymon and Iphigenia from 1884, shows Iphigenia stretched out languidly in her sleep, in the last warm light of the day; behind her the full moon is just starting to rise. Leighton has changed the season to autumn, with the leaves already brown but the days still hot. Cymon stands in shadow on the right, idly scratching his left knee, gazing intently at Iphigenia.
As far as the painters are concerned, that’s it, and you’d presume the couple lived happily ever after. Not according to Boccaccio, though.
When Iphigenia finally awoke, she was surprised to see Cimon there, and recognised him immediately. Cimon insisted on accompanying her to her house, then went to his family home, where he turned a new leaf, and over the period of four years transformed himself into the best-dressed, most cultured and refined young man on Cyprus. Despite this transformation, Cimon was unable to persuade Iphigenia’s father to allow him to marry the young woman, but was told that she was betrothed to a noble on the island of Rhodes. When the time came for her marriage, Cimon took an armed vessel and gave chase to the ship carrying Iphigenia to Rhodes. He boarded her ship and abducted her.
With Iphigenia on board, Cimon headed for the island of Crete, where he and his crew had relatives and friends. But shortly after they had altered course, a storm blew up, so violent that it threatened to sink the ship. Unable to tell where they were heading, they ended up taking shelter off the coast of Rhodes, where they were caught up by the ship from which they had just abducted Iphigenia.
When their vessel ran aground, Cimon and his crew were forced ashore where they were quickly rounded up and thrown into prison, and Iphigenia was returned to her family ready for her wedding. Iphigenia’s fiancé implored the chief magistrate of Rhodes, Lysimachus, to put Cimon to death, but he was held in custody with the rest of his crew. It happened that Lysimachus was deeply in love with a young woman of Rhodes, who was betrothed to Iphigenia’s future brother-in-law. To Lysimachus’ relief, that marriage had been postponed several times, but it was then decided to hold both weddings in the same ceremony.
Lysimachus was aggrieved by this, and decided the only way he could marry the Rhodian woman that he loved was to abduct her. In order to do so, he needed the help of Cimon and his crew, who would undoubtedly be delighted to be able to abduct Iphigenia again. Lysimachus offered Cimon a deal whereby they would together make off with their partners from the scene of the joint wedding, and they agreed to proceed with that.
Two days later, at dusk, as the weddings were just getting under way, Lysimachus, Cimon and his crew entered the house of the two bridegrooms and seized their brides. Unfortunately, the grooms were armed and mounted a determined resistance. Cimon killed Iphigenia’s fiancé with a single blow to the head, and the other woman’s intended husband fell dead following a blow by Lysimachus.
Lysimachus, Cimon, their crew and the two abducted brides then fled to a ship which they sailed to exile in Crete, where the two couples were married, amid great and joyous celebrations. In time, the people of Cyprus and Rhodes forgave them for the violent way they had stolen their brides; Lysimachus and his wife were able to return to Rhodes, and Cimon and Iphigenia returned to live happily ever after on Cyprus.
None of which was even hinted at by those paintings, however wonderful they are.