Robotic hand helps pianists overcome “ceiling effect”
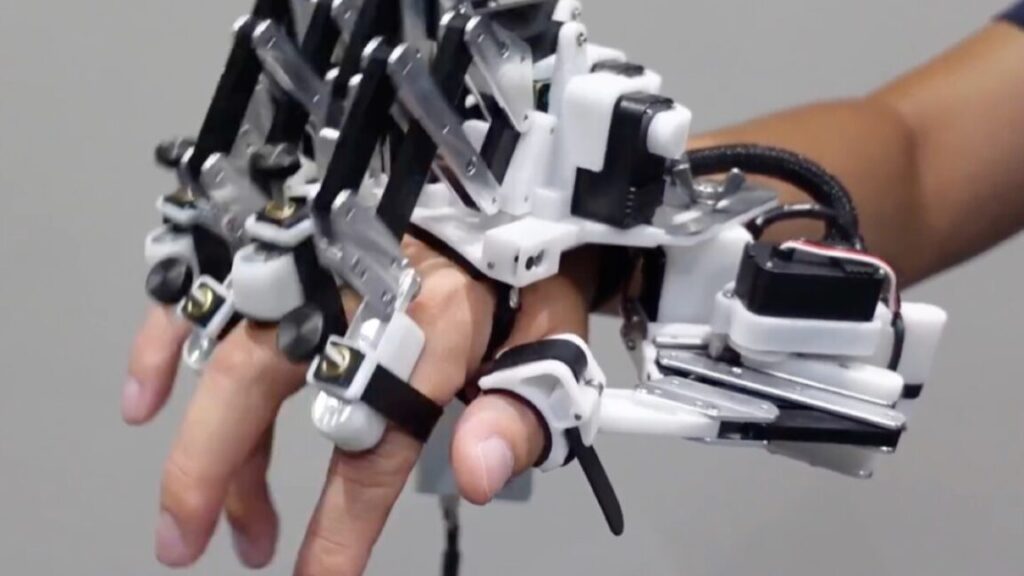
When it comes to fine-tuned motor skills like playing the piano, practice, they say, makes perfect. But expert musicians often experience a “ceiling effect,” in which their skill level plateaus after extensive training. Passive training using a robotic exoskeleton hand could help pianists overcome that ceiling effect, according to a paper published in the journal Science Robotics.
“I’m a pianist, but I [injured] my hand because of overpracticing,” coauthor Shinichi Furuya of Kabushiki Keisha Sony Computer Science Kenkyujo told New Scientist. “I was suffering from this dilemma, between overpracticing and the prevention of the injury, so then I thought, I have to think about some way to improve my skills without practicing.” Recalling that his former teachers used to place their hands over his to show him how to play more advanced pieces, he wondered if he could achieve the same effect with a robotic hand.
So Furuya et al. used a custom-made exoskeleton robot hand capable of moving individual fingers on the right hand independently, flexing and extending the joints as needed. Per the authors, prior studies with robotic exoskeletons focused on simpler movements, such as assisting in the movement of limbs stabilizing body posture, or helping grasp objects. That sets the custom robotic hand used in these latest experiments apart from those used for haptics in virtual environments.