Changing Paintings: 62 Aeneas flees Troy
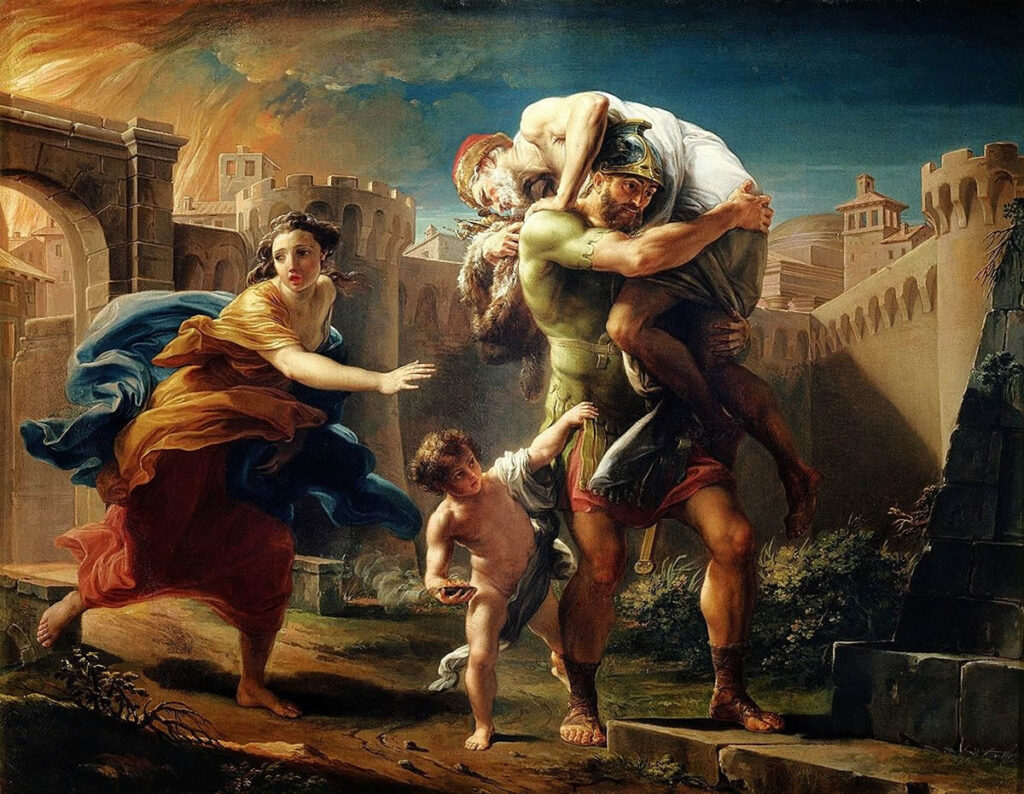

Ovid assures us that the Fates didn’t completely crush the hopes of Troy in its destruction: from within the burning ruins, the hero Aeneas is fleeing, his aged father on his shoulders, and with his son Ascanius. For a Roman reader, Aeneas needs no introduction; like so many classical heroes, he’s the product of a union between a god and a mortal. His case is unusual, as it wasn’t Jupiter to blame, and Aeneas’ father was the mortal Anchises, now being carried on the shoulders of his son, and his mother was the goddess Venus.
William Blake Richmond (1842–1921), Venus and Anchises (1889-90), oil on canvas, 148.6 x 296.5 cm, Walker Art Gallery, Liverpool, England. Wikimedia Commons.
Venus and Anchises, painted by William Blake Richmond between 1889-90, shows this legend. Jupiter challenged Cupid to shoot an arrow at his mother, causing her to fall in love with Anchises when she met him herding his sheep on Mount Ida. Aeneas was the result of that union, and the legend is the explanation for Venus watching over the safety of Aeneas during his prolonged journey from Troy.
There have been many fine paintings of Aeneas fleeing the sacked city with his family.
Adam Elsheimer (1578–1610), Aeneas Saving Anchises from Burning Troy (date not known), gouache on paper, 14.3 × 9.7 cm, Private collection. Wikimedia Commons.
Unusually, one of Adam Elsheimer’s paintings of Aeneas Saving Anchises from Burning Troy was made in gouache. Of all these depictions, this seems to be the only one based on a reconstruction with models, as the method of carrying is not only feasible, but practical. Note how Aeneas is grasping a robe acting as his father’s seat, and Anchises has interlocked his fingers on his son’s forehead.
Adam Elsheimer (1578–1610), The Burning of Troy (c 1600-01), oil on copper, 36 x 50 cm, , Alte Pinakothek, Munich, Germany. Wikimedia Commons.
That doesn’t, though, appear to have been a study for Elsheimer’s finished work The Burning of Troy (c 1600-01) painted in oil on copper. The pair, with young Ascanius and his mother to the right, are seen in the left foreground. Elsheimer’s backdrop of the burning city includes the Trojan Horse, to the left of the upper centre, and hints with subtlety at the vast tragedy taking place.
Simon Vouet (1590-1649), Aeneas and his Father Fleeing Troy (c 1635), oil on canvas, dimensions not known, San Diego Museum of Art, San Diego, CA. Image by Wmpearl, via Wikimedia Commons.
Simon Vouet’s Aeneas and his Father Fleeing Troy from about 1635 shows the family group in close-up. From the left are Creusa, Aeneas’ wife who dies before she can leave the city, Aeneas, Anchises, and a very young Ascanius. This is the start of their flight, as Aeneas and Creusa are persuading Anchises to let Aeneas carry him to safety.
Pompeo Batoni (1708–1787), Aeneas Fleeing from Troy (1753), oil on canvas, 76.7 × 97 cm, Galleria Sabauda, Turin, Italy. Wikimedia Commons.
Pompeo Batoni’s Aeneas Fleeing from Troy (1753) shows the family as they leave the burning city behind them. Creusa is already falling slightly behind, and looks particularly distressed.
Oddly, Ovid doesn’t mention Creusa’s fate in the Metamorphoses, although a Roman reader would have been well aware of the detail in Virgil’s Aeneid, where she is left behind. By the time the hero reaches the city gates with his father and son, his wife is nowhere to be seen. Aeneas re-enters the burning city to look for her, but her ghost tells him that his destiny is to reach Hesperia, where he will become a king and marry a princess.
Aeneas, Anchises and Ascanius then sail with a fleet of Trojan survivors to reach Delos, site of a temple to Apollo, whose priest and ruler of the island is Anius. He shows them the temple and city, and the two trees that the goddess Latona had held onto when she gave birth to the twin deities Apollo and Diana.
Johann Wilhelm Baur (1600-1640), Aeneus Meets Anius (c 1639), engraving for Ovid’s Metamorphoses, further details not known. Wikimedia Commons.
Johann Wilhelm Baur’s engraving of Aeneus Meets Anius (c 1639), for an illustrated edition of Ovid’s Metamorphoses, might appear generic, but is actually carefully composed. Aeneas stands upright, his spear almost vertical, in its centre. To the right his father Anchises embraces his old friend Anius, and to the left is the young Ascanius. In the right background is the city, with its imposing temple at the edge.
Claude Lorrain (1604/1605–1682), Landscape with Aeneas at Delos (1672), oil on canvas, 99.6 x 134.3 cm, The National Gallery, London. Wikimedia Commons.
This singular painting is Claude Lorrain’s Landscape with Aeneas at Delos from 1672. This was the first of half a dozen works that Claude painted in the final decade of his life, based primarily on Virgil’s account in the Aeneid. Its meticulous details are supported by a coastal landscape of great beauty.
The twin trees at its centre, an olive and palm according to myth, are those that Latona held when she gave birth to Apollo and Diana, and now provide shade for a shepherd and his flock of sheep.
Claude Lorrain (1604/1605–1682), Landscape with Aeneas at Delos (detail) (1672), oil on canvas, 99.6 x 134.3 cm, The National Gallery, London. Wikimedia Commons.
The king and priest Anius is at the left of the group, wearing priestly white, and pointing out the twin trees to his guests. To his right is Anchises in blue, then Aeneas holding his spear, and his young son Ascanius, with a suitably shorter spear in his right hand.
Claude’s fine details tell further stories too.
Claude Lorrain (1604/1605–1682), Landscape with Aeneas at Delos (detail) (1672), oil on canvas, 99.6 x 134.3 cm, The National Gallery, London. Wikimedia Commons.
The relief at the top of the temple, immediately below a couple of casual onlookers, tells the story of Latona’s twins killing the giant Tityus, who had tried to rape their mother. Tityus is seen at the right of the relief, fallen down and wounded by the arrows of Diana (centre) and Apollo (left). Similarly to the Titan Prometheus, Tityus was sentenced to spend his time in the Underworld with two vultures feeding on his liver, which regenerated each night.
Anius then entertains his guests to a feast in their honour. Anchises asks what happened to Anius’ four daughters and one son. Anius replies that he is now almost childless, with his son far away on the island of Andros, and his daughters taken from him by Agamemnon. Bacchus had given his girls the remarkable gift that whatever they touched was transformed into food, wine, and oil. Because of that, the Greeks departing from their conquest of Troy abducted them to feed their army. When the daughters begged Bacchus to release them, the god turned them into white doves of Venus, Aeneas’s mother.
Anius and his guests continue to tell tales before retiring to sleep for the night. In the morning Aeneas goes to the oracle of Phoebus, who cryptically tells him to seek his ancient mother, and head for ancestral shores. They then exchange gifts, including a decorated krater (wine bowl) telling another story. The image on the krater shows the death of Orion’s daughters in Thebes. Their funeral procession took the bodies to the great square, for their cremation on pyres. From their ashes rose twins known as the Coroni.
After that, Aeneas and his companions sail on to Crete.