Urban Revolutionaries: 8 The Oldest Profession

Prostitution isn’t the only occupation that has been claimed to be the earliest, and that claim wasn’t even made until the late nineteenth century. However, it certainly was one of the most common ways for women to earn a living in the growing cities of Europe during the nineteenth century. Like bars and places of entertainment, prostitution only thrived where there were plenty of potential customers with money. London and Paris were renowned for the number of women who worked as prostitutes, catering for all classes and pockets.
John Roddam Spencer Stanhope (1829–1908), Thoughts of the Past (1859), oil on canvas, 86.4 x 50.8 cm, The Tate Gallery (Presented by Mrs F. Evans 1918), London. © The Tate Gallery and Photographic Rights © Tate (2016), CC-BY-NC-ND 3.0 (Unported), http://www.tate.org.uk/art/artworks/stanhope-thoughts-of-the-past-n03338
Thoughts of the Past (1859) was the first of John Roddam Spencer Stanhope’s paintings to be exhibited at the Royal Academy, and remains one of his best-known works. It shows a woman standing by a window looking out onto the River Thames in London, and is a faithful depiction of the studio below that used by Dante Gabriel Rossetti at the time, in Chatham Place.
The woman and her surroundings contain rich clues as to her status: behind her, a gaudy cloak with some white lace hangs. The small dressing table is tatty and covered with cheap, garish jewellery. Potted houseplants straggle up for light from the window, and at their foot is a man’s glove and walking stick. She’s dressed for the bedroom, with her long red hair let down, and looks gaunt, her eyes tired and sunken. The view looks towards Waterloo Bridge, with the Strand embankment to the right, at the time a popular haunt for prostitutes.
Ford Madox Brown (1821–1893), Work (1863), oil on canvas, 68.4 x 99 cm, Birmingham Museum and Art Gallery, Birmingham, England. Wikimedia Commons.
In Ford Madox Brown’s Work (1863), the profligate woman in the foreground wears a torn and tattered red dress (detail below), although it’s faded rather than full scarlet. With her gaggle of unruly children and a babe in arms, she’s portrayed as a prostitute.
Ford Madox Brown (1821–1893), Work (detail) (1863), oil on canvas, 68.4 x 99 cm, Birmingham Museum and Art Gallery, Birmingham, England. Wikimedia Commons.
Henri Gervex (1852–1929), Rolla (1878), oil on canvas, 175 x 220 cm, Musée des Beaux-Arts, Bordeaux, France. Wikimedia Commons.
Like Manet’s notorious Olympia (1863) before, the contemporary surroundings and heap of clothes beside Henri Gervex’s Rolla (1878) ensured it was deemed immoral by the Salon jury. This was inspired by a poem by Alfred de Musset about a prostitute, and Gervex depicted her asleep in bed as her client gets dressed the following morning. In the end, the artist got a commercial gallery to exhibit this painting, where it attracted far more attention than it would have in the Salon.
Jean-Louis Forain (1852–1931), The Client (1878), watercolour, gouache and pencil, 24.8 x 32.4 cm, Dixon Gallery and Gardens, Memphis, TN. The Athenaeum.
Jean-Louis Forain’s candid view of endemic prostitution shown in his watercolour The Client (1878) surpassed those of Edgar Degas, and were later to inspire the paintings of Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec (1864-1901).
Félicien Rops (1833–1898), Down and Out (1882), pastel and crayon on paper, 45.5 x 30 cm, Musée Provincial Félicien Rops, Namur, Belgium. Wikimedia Commons.
One response to the popularity of Naturalism was Félicien Rops’ tender portrait of a low-end prostitute Down and Out in 1882. While she stands next to a sheet on the wall headed TARIF making clear her trade, a single small red flower adorns her flaunted cleavage.
Antonino Gandolfo (1841–1910), Compensation (1880-85), oil on canvas, 84 x 51 cm, location not known. Image by Luigi Gandolfo, via Wikimedia Commons.
In Antonino Gandolfo’s Compensation from 1880-85, the man settling his bill is only seen by the hand holding out money, and a foot. The young woman holding out her hand to receive, looks away in shame, and wears scarlet to advertise her trade. This is one of a series by Gandolfo depicting the poor in the city of Catania on Sicily.
The theme of prostitution dominates many of the paintings of the Norwegian artist Christian Krohg, who was also an author.
Christian Krohg (1852–1925), Albertine in the Police Doctor’s Waiting Room (1885-87), oil on canvas, 211 x 326 cm, Nasjonalgalleriet, Oslo, Norway. Wikimedia Commons.
Just before Christmas 1886, Christian Krohg’s first novel Albertine was published by a left-wing publisher. Its central theme is prostitution in Norway at the time, and the police quickly seized all the copies they could find, banning it on the grounds of violating the good morals of the people. Krohg was found guilty of the offence the following March and fined, although the police were only able to seize 439 of the first 1600 copies to go into circulation.
At the same time as he was writing that novel, Krohg had been working on his largest and most complex painting: Albertine in the Police Doctor’s Waiting Room (1885-87). He also painted other scenes from the book.
In the novel, Albertine starts as a poor seamstress, who is mistaken for a prostitute by the police officer in charge of the section controlling prostitutes. He plies her with alcohol then rapes her. She is summoned to be inspected by the police doctor, whose examination further violates her, making her think that she is destined to be a prostitute, and that is, of course, exactly what happens.
Albertine isn’t the prominent woman in the centre looking directly at the viewer: Krohg’s heroine is the simple and humble country girl at the front of the queue to go into the police doctor for inspection. Behind her is a motley line of women from a wide range of situations. At the right, in the corner of the room, is another country girl with flushed cheeks. Others are apparently more advanced in their careers, and stare at Albertine, whose profiled face is barely visible from behind her headscarf. Barring the way to the surgery door, and in control of the proceedings, is a policeman.
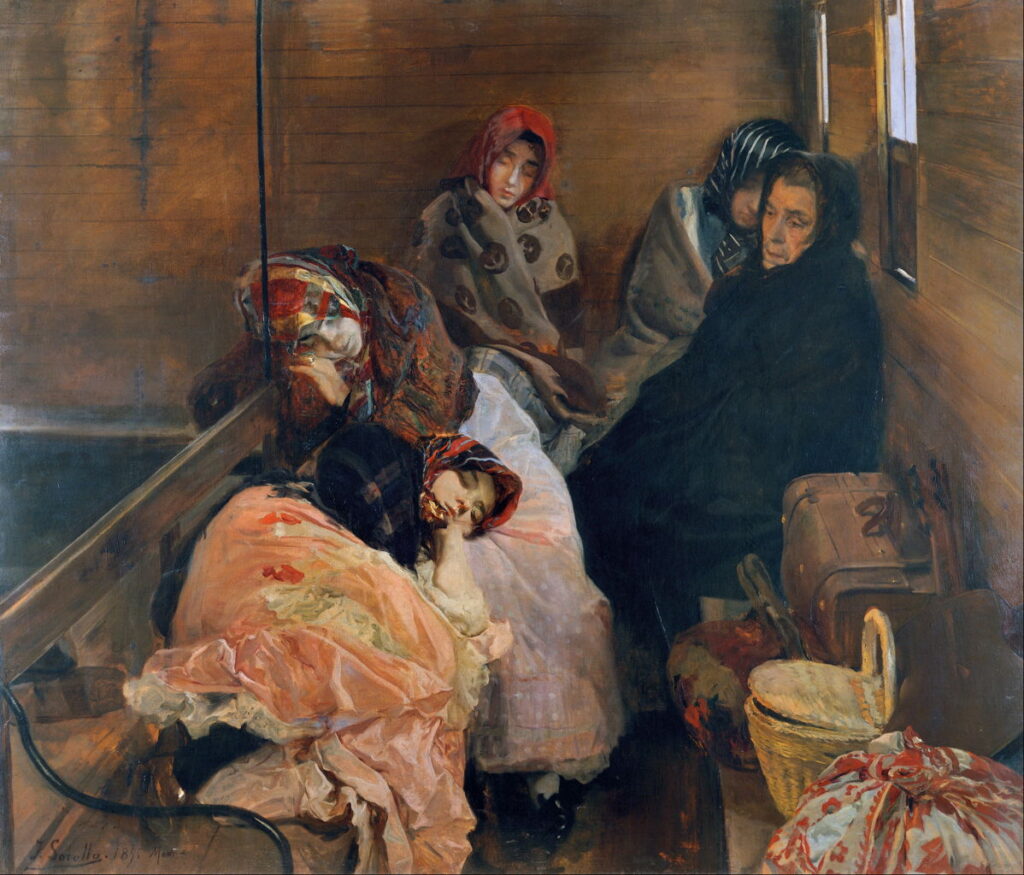
Joaquín Sorolla y Bastida (1863–1923), White Slave Trade (1895), oil on canvas, 166.5 x 194 cm, Museo Sorolla, Madrid, Spain. Wikimedia Commons.
During Joaquín Sorolla’s period of Naturalist painting, he depicted the contemporary trade in prostitutes in Spain. His White Slave Trade (1895) is set in a bleak railway compartment, where four young women are asleep while being transported in the care of an older woman. In contrast to their guardian who wears black, the young women are dressed in bright-coloured Valencian regional costumes, and wear fashionable shoes. Their few possessions are stacked on the bench at the right, and include a guitar. The ‘slave trade’ to which the title refers is the movement of prostitutes between brothels, in this case from the city of Valencia to the port of Cartagena, then over to Orán and Algeria.
Aksel Waldemar Johannessen was another Norwegian who took up the cause with Krohg. He had been born in Hammersborg, a poor suburb of Oslo, but his paintings weren’t exhibited until after his death in 1922.
Aksel Waldemar Johannessen (1880–1922), Forced into Prostitution (1915), oil on canvas, 41 × 31 cm, Private collection. Wikimedia Commons.
Forced into Prostitution, also known as Night Wanderer, from 1915, shows the artist’s wife Anna in the role of a prostitute in the city of Oslo. Here an odious-looking client with bushy eyebrows and a thick-set face is pressing against her from behind, wanting to pick her up.