Changing Paintings: 74 The Age of Augustus

With Julius Caesar transformed into a star following his assassination, Ovid ends the last book of his Metamorphoses with praise of the contemporary Emperor Augustus, and expresses his own aspirations to immortality.
Jupiter foretells some of the accomplishments of Caesar’s adopted heir, Augustus, who was then still known as Octavius or Octavian. These include successes in battle, the fall of Cleopatra, Queen of Egypt, and the growth of the Roman Empire. Ovid then looks ahead to Augustus’ own future apotheosis, when he will become a god. Finally, the author wishes for his words to be read throughout the empire, and to live on in fame.
Louis Gauffier (1762–1801), Cleopatra and Octavian (1787), oil on canvas, 83.8 x 112.5 cm, Scottish National Gallery, Edinburgh, Scotland. Wikimedia Commons.
Cleopatra’s legendary beauty has been expressed in paint by several artists, among them Louis Gauffier, whose Cleopatra and Octavian of 1787 shows the young Augustus and Queen Cleopatra conversing under the watchful eye of Julius Caesar’s bust. Cleopatra allied herself with Antony, and was eventually defeated at the Battle of Actium, ending years of civil war in Rome. Antony fell on his sword, and Cleopatra is reputed to have killed herself with the bite of an asp.
Jean-Léon Gérôme (1824–1904), The Age of Augustus, the Birth of Christ (c 1852-54), oil on canvas, dimensions not known, location not known. Image by Wmpearl, via Wikimedia Commons.
It’s Jean-Léon Gérôme who reminds us of the great events that were taking place at the eastern end of the Mediterranean during the reign of Augustus, in The Age of Augustus, the Birth of Christ (c 1852-54). The emperor sits on his throne, overseeing a huge gathering of people from all over the Roman Empire. Grouped in the foreground in a quotation from a traditional nativity is the Holy Family, whose infant son was to transform the empire in the centuries to come. Sadly for Ovid, and even Virgil, Gérôme’s throng doesn’t appear to include distinguished poets from the Augustan age.
Jean-Joseph Taillasson (1745—1809), Virgil reading the Aeneid to Augustus and Octavia (1787), oil on canvas, 147.2 × 166.9 cm, The National Gallery (Bought, 1974), London. Courtesy of and © The National Gallery, London.
Several painters have, though, shown Augustus’ favourite Virgil at the emperor’s court. Jean-Joseph Taillasson’s Virgil reading the Aeneid to Augustus and Octavia from 1787 shows the poet at the left, holding a copy of his Aeneid, reading a passage to the emperor Augustus and his sister Octavia. Augustus has been moved to tears by the passage praising Octavia’s dead son Marcellus, and his sister has swooned in her emotional response.
Artist not known, The Great Cameo of France (c 50 CE), five-layered sardonyx cameo, 31 x 26.5 cm, Cabinet des médailles, Bibliothèque nationale de France, Paris. Image by Jastrow and Janmad, via Wikimedia Commons.
Ovid was in no position to commit Augustus’ eventual death and apotheosis to verse, but this is shown in an exquisite sardonyx cameo known as The Great Cameo of France from the first century CE. Augustus is here being brought up to the gods at the top of the scene.
Giovanni Battista Tiepolo (1696–1770), Maecenas Presenting the Liberal Arts to Emperor Augustus (1743), oil on panel, 70 x 89 cm, Hermitage Museum Государственный Эрмитаж, Saint Petersburg, Russia. Wikimedia Commons.
Although a fan of Virgil and a minor author in his own right, Augustus wasn’t a strong patron of the arts. Until 8 BCE, his friend Gaius Maecenas acted as cultural advisor to Augustus, and was a major patron of Virgil. Tiepolo’s Maecenas Presenting the Liberal Arts to Emperor Augustus from 1743 shows Maecenas at the left introducing an anachronistic woman painter and other artists to the emperor.
Ovid’s major patron was Marcus Valerius Messalia Corvinus, and is thought to have been friends with poets in the circle of Maecenas. But all this became irrelevant when Ovid offended Augustus, and in 8 CE was banished to Tomis, on the western coast of the Black Sea, at the north-eastern edge of the Roman Empire.
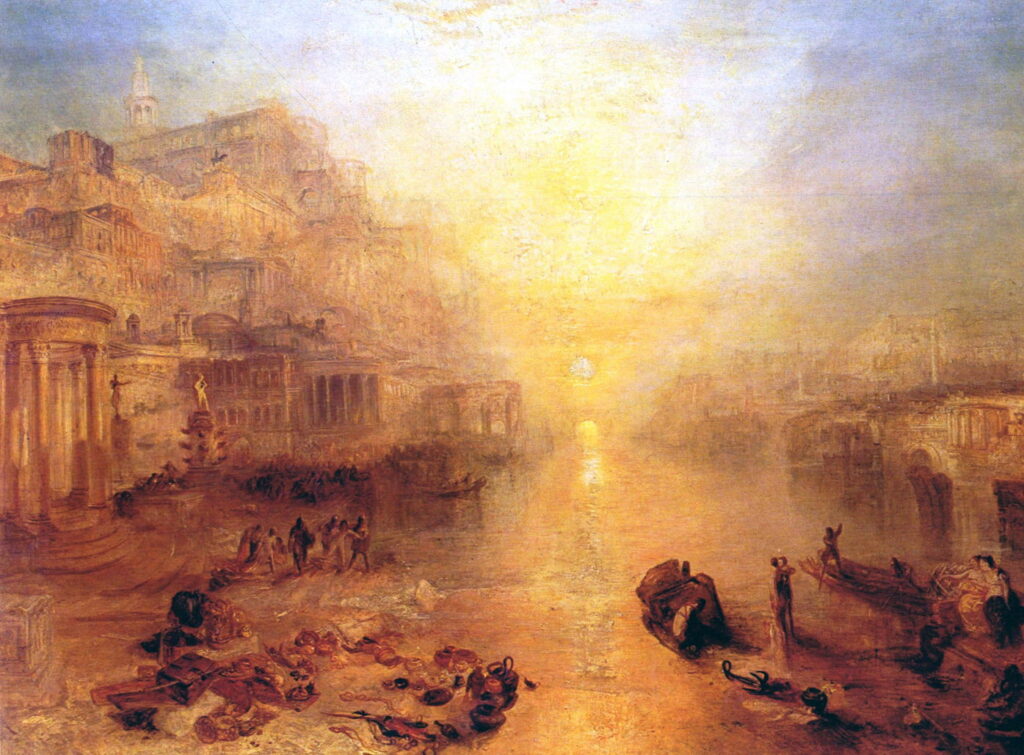
Joseph Mallord William Turner (1775–1851), Ancient Italy – Ovid Banished from Rome (1838), oil on canvas, 94.6 x 125 cm, Private collection. Wikimedia Commons.
It is perhaps JMW Turner who has best captured this in his Ancient Italy – Ovid Banished from Rome, exhibited in 1838. In a dusk scene more characteristic of Claude Lorrain’s contre-jour riverscapes, Turner gives a thoroughly romantic view of Ovid’s departure by boat from the bank of the Tiber.
Ovid died in Tomis in 17 or 18 CE, and by a quirk of fate his banishment from the city of Rome wasn’t formally revoked until 2017, two millennia later.
But Ovid saw his road to immortality not by apotheosis, rather through his work being read, and living on in the minds of those countless readers. In that, he undoubtedly succeeded: his Metamorphoses and other poems continue to be read, both in their original Latin and in translation into many languages, and depicted in many great paintings.