Ancient desert mega-structures were planned using carved maps to scale

There’s rarely time to write about every cool science-y story that comes our way. So this year, we’re once again running a special Twelve Days of Christmas series of posts, highlighting one science story that fell through the cracks in 2020, each day from December 25 through January 5. Today: Archaeologists found two stone engravings in Jordan and Saudi Arabia that may represent the oldest architectural plans for desert kites.
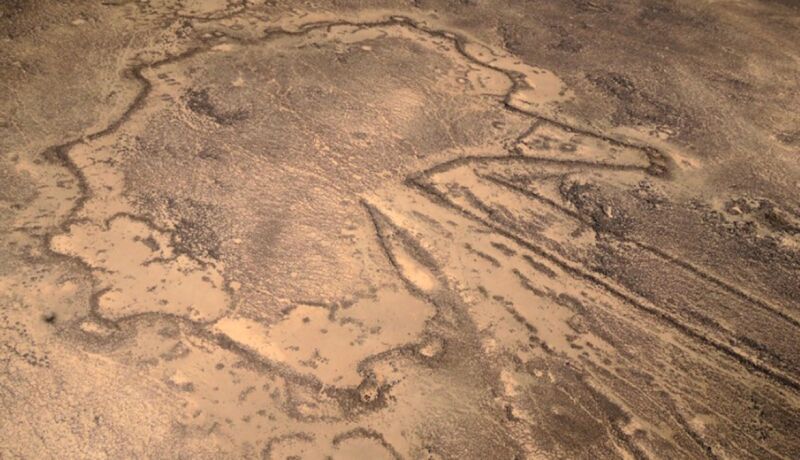
During the 1920s, aerial photographs revealed the presence of large kite-shaped stone wall mega-structures in deserts in Asia and the Middle East that most archaeologists believe were used to herd and trap wild animals. More than 6,000 of these “desert kites” have been identified as of 2018, although very few have been excavated. Archaeologists found two stone engravings—one in Jordan, the other in Saudi Arabia—that they believe represent the oldest architectural plans for these desert kites, according to a May paper published in the journal PLoS ONE.
“The discovery of these very ancient representations highlights the question of the methods used by kite builders,” the authors wrote. “Kites are large material structures that could not be designed without what we call today planning. The ability to transpose large spaces into a small two-dimensional surface represents a milestone in intelligent behavior. Such structures are visible as a whole only from the air, yet this calls for the representation of space in a way not seen at this time.”